February 7, 2024
6 Trends for the Future of Textiles from Heimtextil
Textile trends and technology intersected at this year’s Heimtextil, the massive global fair for textiles at Messe Frankfurt in Germany. The trend space curated by SPOTT was the soul of the show, weaving developments from around the world together in an expressive, cohesive context for designers, dealers, and specifiers—informing colors, styles, textures, and approaches to sustainability.
This addresses Heimtextil’s overarching theme, New Sensitivity, not only in the obvious sense of touch, sensation, and spirituality, but also in the impact of creating products and how it affects the humans using these textiles in residential and contract spaces. Recycling, upcycling, and circularity have never loomed so large, even though the fair has promoted sustainability for years.
It seems so long ago—in fact, it was prepandemic—that we marveled at displays on long tables holding examples of alternative sustainable materials, like “leathers” made out of banana skins. These novelties now are scalable, with many more resources in production. Even in the world of textiles, issues like climate change, biodiversity, mental health, and digitization are part of the conversation. Here are four trends for the future of textiles from Heimtextil:
66% of all American textile waste in 2018 ended up in the landfill. That’s 11,300 tons, and represented 7.7% of all landfill waste that year.
“Textiles: Material-Specific Data,” U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Unconventional Plant-based Textiles
These are textiles made from plant crops, like cactus, hemp, abaca, seaweed, and rubber, or plant by-products. We met a fifth-generation pineapple farmer from India, for example, who now is converting waste from his own family’s crop into a soft wool-like fiber that can be spun into fabric.
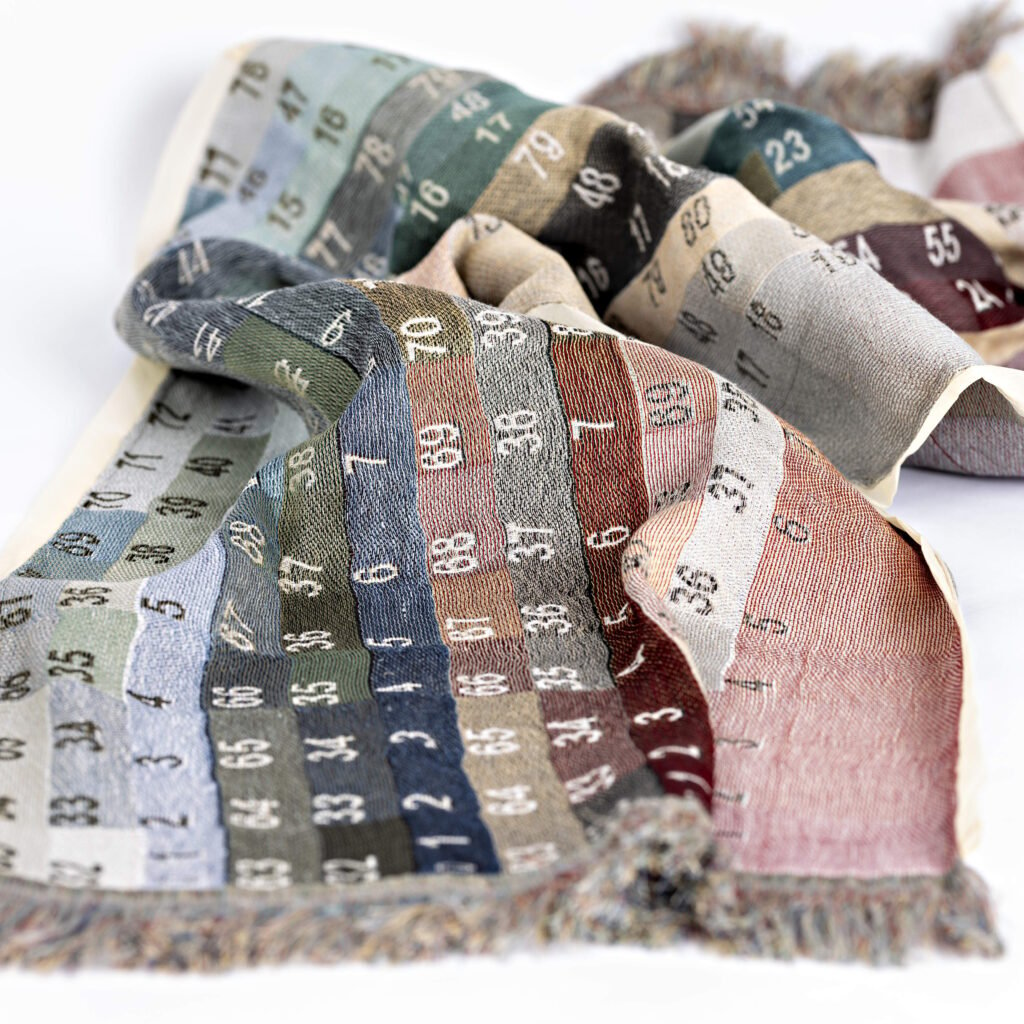







Textile Technologies Focus on Resource Use
Construction and design technologies are tapping into upcycling and recycling, reducing our reliance on virgin materials. We’re also seeing exciting new methods like 3D knitting, which can substitute for weaving and lead to less fabric waste. Alternately, there are weaving techniques that allow the creation of multi-colored weaves with only a few yarns.
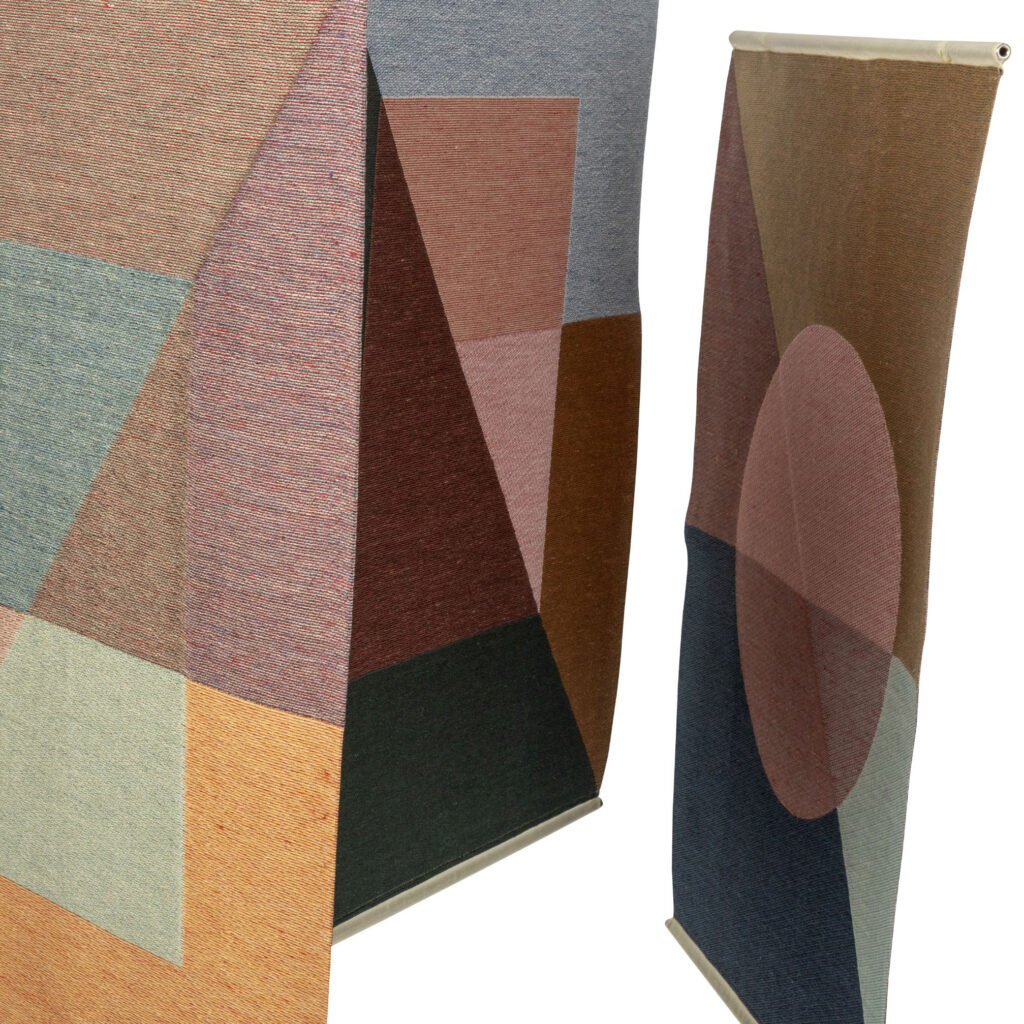
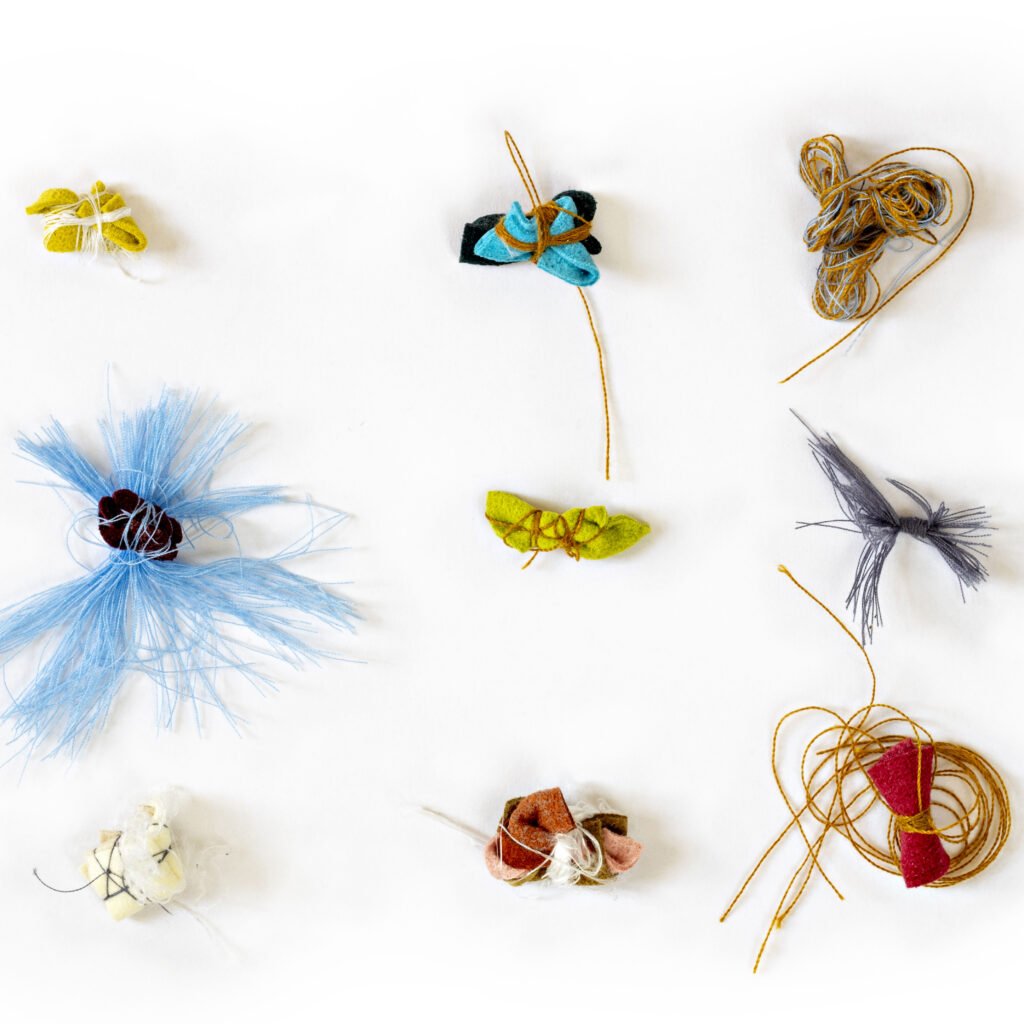


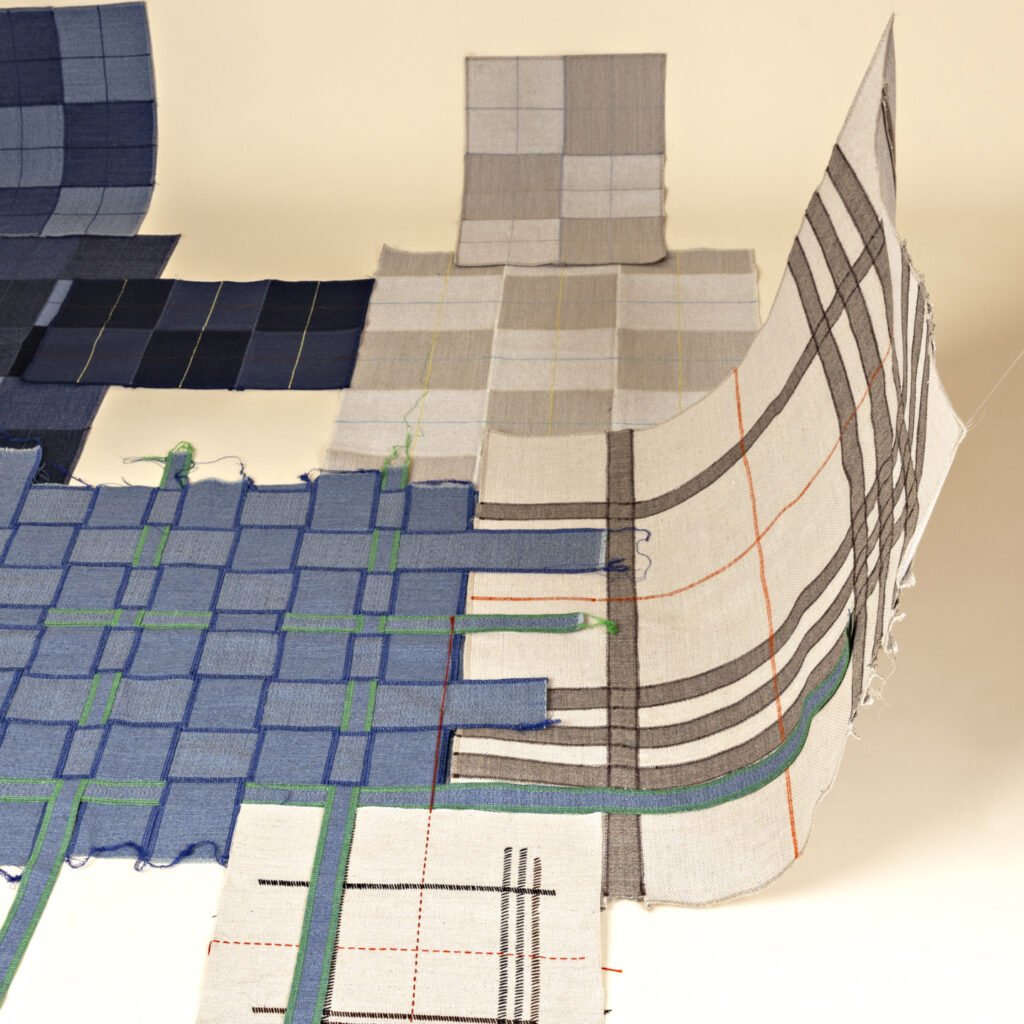



Bioengineered Textiles Catch on
This is a fusion between nature and technology. Instead of growing plants and extracting fibers, the textiles actually are constructed from the protein, carbohydrates or bacteria in corn, grass and cane sugar. A bio-molecular process allows the creation of filaments that are made into yarn. With the same functionality of a synthetic, the product still is biodegradable because of its natural origin.






Textiles Adopt Regenerative Design Principles
In a global showcase by the London-based design futures consultancy FranklinTill, cutting edge materials illustrated the principles of regenerative design—that is, putting back better, creating holistic creative practices that restore or renew resources.
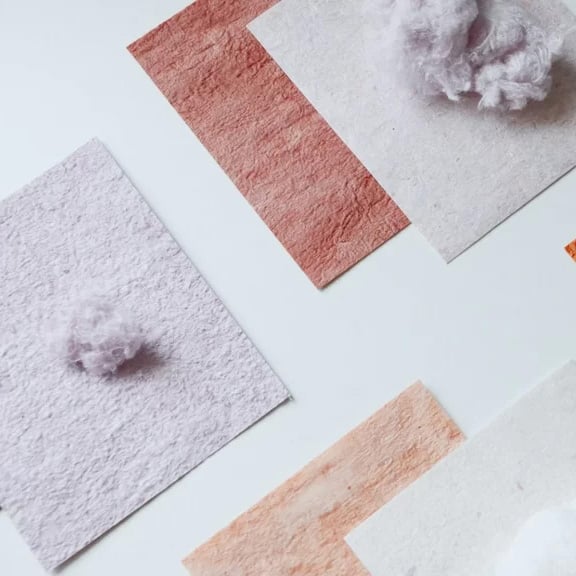



Colors Drawn from The Earth
The trends in materiality and technology in no way stole the thunder from aesthetics. Color palettes featured natural pigments from the earth, including avocado seeds, algae, living bacteria, antique pigments such as raw siena, as well as bio-engineered indigo and cochineal.


Meeting Sustainability Standards
Hotels, restaurants and offices, public buildings, care facilities all have heightened demands for sustainability, and legal requirements are playing an increasing role in their selection of suitable textiles. A curated library at Heimtextil presented functional textiles from exhibitors such as Edmund Bell, Futura Leathers, and Vanelli, focusing on flame retardant, sound-absorbing, lightfast, antimicrobial, dirt repellant amd scrub resistant features.The selection is available online.
“Modern textiles are becoming more efficient and taking on new key functions such as sound insulation, fire protection and hygiene,” says Bettina Bar, show director for Heimtextil.

Would you like to comment on this article? Send your thoughts to: [email protected]
- No tags selected
Latest
Viewpoints
Archtober Invites You to Trace the Future of Architecture
Archtober 2024: Tracing the Future, taking place October 1–30 in New York City, aims to create a roadmap for how our living spaces will evolve.
Projects
Kengo Kuma Designs a Sculptural Addition to Lisbon’s Centro de Arte Moderna
The swooping tile- and timber-clad portico draws visitors into the newly renovated art museum.
Products
These Biobased Products Point to a Regenerative Future
Discover seven products that represent a new wave of bio-derived offerings for interior design and architecture.





